Introduction to Computer Networking
how an application use the Internet
The structure of the Internet:The 4 layer model
The Internet protocol(IP)
Basic architectural ideas and principles:
Packet switching
Layering
Encapsulation
1.1 A Day in the life of an ApplicationDominant model:
bidrectional
reliable byte stream connection
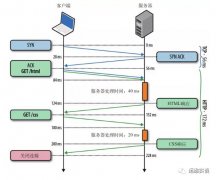
1. World Wide Web (HTTP)C/S架构
发送commands,接收responses
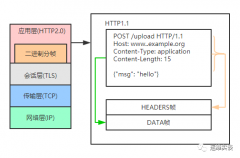
request:"GET / HTTP/1.1"
response: "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
2. BitTorrentP2P架构
break files into "pieces"
所有存有pieces file的client被称为swarm,client join and leave swarms
tracker追踪swarm的成员,通过torrent file向一个tracker获取swarm中的client列表
request: "GET list of clients in swarm"
response: "200 OK list of clients"
3. Skypemixed架构
如果两个client能互联,就在client间建立连接--->P2P
如果有一方存在NAT:Client A-----Internet-----NAT---ClientB
由于NAT,B可以连接A,但A无法连接B
A cannot open connection to B
B在一个Rendezvous上注册,A向Rendezvous发送请求,Rendezvous转发请求给B,B主动和A建立连接
双方均存在NAT
通过一个Relay转发服务器作为中转,转发双方的消息
1.2 What the Internet is: The 4 Layer Internet ModelApplication:(http, bit-torrent)
application-specific semantics
Transport:(tcp, udp)
guarantees correct, in-order delivery of data end-to-end
controls congestion
Network:(IP)
must use the Internet Protocol(IP)
best-effort attempt to deliver datagrams, no promises
IP datagrams can get lost, out of order, and can be corrupted
Link:(802.11, 3G, DSL, Ethernet)
one-hop control
delivers data over a single link between an end host and router, or between routers
two extra things need to know:
IP is the "thin waist"
the 7-layer OSI Model
Application------http--------Application----7
Application------ASCII-----Presentation--6
Transport--------TCP-------Session--------5
Transport--------TCP-------Transport------4
Network----------IP----------Network--------3
Link---------------Ethernet----Link------------2
Link---------------Ethernet----Physical------1
1.3 What the Internet is: The IP service modelThe Internet Protocol(IP)
Transport Segment
IP Datagram
Link Frame
The IP service Model
Property BehaviorDatagram Hop by hop routing
Unreliable Packets might be dropped because of full wait queue
Best effort
Connectionless No per-flow state. Might be mis-sequenced
why simple?
faster, more streamlined and lower cost to build and maintain
The end-to-end principle: implement features in the end hosts if possible
Allows a variety of reliable(or not) services to be built on top
Works over any link layer: IP makes very few assumptions about the link layer below
The IP service model
Tries to prevent packets looping forever(TTL, time to live)
Will fragment packets if they are too long
Uses a header checksum to reduce chances of delivering datagram to wrong destination
Allows for new versions of IP
IPv4: 32 bit
IPv6: 128 bit
Allows for new options to be added to header
Quiz:
In an alternative to the Internet Protocol called "ATM" proposed in the 1990s, the source and destination address is replaced by a unique "flow" identifier that is dynamically created for each new end-to-end communication. Before the communication starts, the flow identifier is added to each router along the path, to indicate the next hop, and then removed when the communication is over. Which of the following statements are implications of this design? Check all that apply.
(+)There is state in the network for every communication flow, rather than just for every destination.
(-)If a link fails, there is no need to update any state in the network.
(-)There must be a centralized controller to manage the insertion and removal of identifiers, as well as update them whenever a flow needs to be re-routed.
(-)It means we no longer need a transport layer to reliably deliver correct, in-order data to applications.
cs244a-Introduction to Computer Networking-Unit1
温馨提示: 本文由杰米博客推荐,转载请保留链接: https://www.jmwww.net/file/web/10310.html
- 上一篇:js最底层的那些事
- 下一篇:自己动手搭建经典的3层 Asp.Net MVC