httpclient与webapi
System.Net.Http 是微软推出的最新的 HTTP 应用程序的编程接口, 微软称之为“现代化的 HTTP 编程接口”, 主要提供如下内容:
1. 用户通过 HTTP 使用现代化的 Web Service 的客户端组件;
2. 能够同时在客户端与服务端同时使用的 HTTP 组件(比如处理 HTTP 标头和消息), 为客户端和服务端提供一致的编程模型。
命名空间 System.Net.Http 以及 System.Net.Http.Headers 提供了如下内容:
1. HttpClient 发送和接收 HTTP 请求与响应;
2. HttpRequestMessage and HttpResponseMessage 封装了 RFC 2616 定义的 HTTP 消息;
3. HttpHeaders 封装了 RFC 2616 定义的 HTTP 标头;
4. HttpClientHandler 负责生成HTTP响应消息的HTTP处理程序。
System.Net.Http 能够处理多种类型的 RFC 2616 定义的 HTTP 实体正文, 如下图所示:
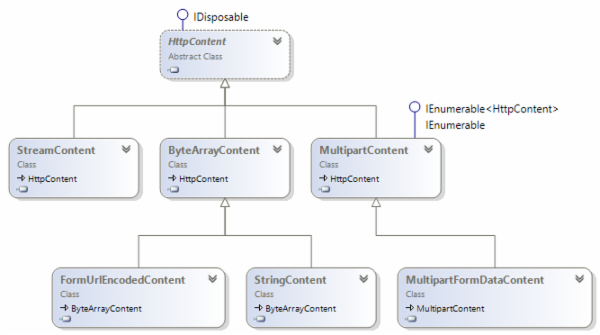
此外, System.Net.Http 对 HTTP 消息的处理采用了职责链模式, 这里有一遍不错的介绍 , 这里就不再多说了。
System.Net.Http 最早是和 Asp.Net Mvc4 同时出现, 是一个第三方组件,名称是 Microsoft HTTP Client Libraries ,可以在 .Net 4.0 中使用。 随着 .Net 4.5 的发布, System.Net.Http 正式成为 .Net 基础类库, 目前已经可以在 .Net 4.0/4.5 、 Windows Phone 、 以及 Windows Store App 中使用。HttpClient 组件类实例为一个会话发送 HTTP 请求。 HttpClient 实例设置为集合会应用于该实例执行的所有请求。 此外,每 HttpClient 实例使用自己的连接池, 隔离其他 HttpClient 实例的执行请求。 HttpClient 也是更具体的 HTTP 客户端的基类。
默认情况下,使用 HttpWebRequest 向服务器发送请求。 这一行为可通过在接受一个HttpMessageHandler实例作为参数的构造函数重载中指定不同的通道来更改。
如果需要身份验证或缓存的功能,WebRequestHandler 可使用配置项和实例传递给构造函数。 返回的处理程序传递到采用 HttpMessageHandler 参数的某构造进行返回参数传递。
如果使用 HttpClient 和相关组件类的 app 在 System.Net.Http 命名空间用于下载大量数据 (可达 50 MB 或更多),则应用程序应这些下载的流和不使用默认值缓冲区。 如果使用默认值缓冲区客户端内存使用量会非常大,可能会导致显着降低的性能。
代码使用,httpclient封装,.net4.0之后:
using Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.UnitTesting; using TestMvc; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Net; using System.Net.Http; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace TestMvc.Tests { [TestClass()] public class ResultFilterTests { [TestMethod()] public void OnResultExecutedTest() { Assert.Fail(); } } class Test { /// <summary> /// HttpClient实现Get请求 /// </summary> static async void dooGet() { string url = ":52824/api/register?id=1&leval=5"; //创建HttpClient(注意传入HttpClientHandler) var handler = new HttpClientHandler() { AutomaticDecompression = DecompressionMethods.GZip }; using (var http = new HttpClient(handler)) { //await异步等待回应 var response = await http.GetAsync(url); //确保HTTP成功状态值 response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode(); //await异步读取最后的JSON(注意此时gzip已经被自动解压缩了,因为上面的AutomaticDecompression = DecompressionMethods.GZip) Console.WriteLine(await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync()); } } /// <summary> /// HttpClient实现Post请求 /// </summary> static async void dooPost() { string url = ":52824/api/register"; var userId = "1"; //设置HttpClientHandler的AutomaticDecompression var handler = new HttpClientHandler() { AutomaticDecompression = DecompressionMethods.GZip }; //创建HttpClient(注意传入HttpClientHandler) using (var http = new HttpClient(handler)) { //使用FormUrlEncodedContent做HttpContent var content = new FormUrlEncodedContent(new Dictionary<string, string>() { {"", userId}//键名必须为空 }); //await异步等待回应 var response = await http.PostAsync(url, content); //确保HTTP成功状态值 response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode(); //await异步读取最后的JSON(注意此时gzip已经被自动解压缩了,因为上面的AutomaticDecompression = DecompressionMethods.GZip) Console.WriteLine(await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync()); } } /// <summary> /// HttpClient实现Put请求 /// </summary> static async void dooPut() { var userId = "1"; string url = ":52824/api/register?userid=" + userId; //设置HttpClientHandler的AutomaticDecompression var handler = new HttpClientHandler() { AutomaticDecompression = DecompressionMethods.GZip }; //创建HttpClient(注意传入HttpClientHandler) using (var http = new HttpClient(handler)) { //使用FormUrlEncodedContent做HttpContent var content = new FormUrlEncodedContent(new Dictionary<string, string>() { {"", "数据"}//键名必须为空 }); //await异步等待回应 var response = await http.PutAsync(url, content); //确保HTTP成功状态值 response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode(); //await异步读取最后的JSON(注意此时gzip已经被自动解压缩了,,因为上面的AutomaticDecompression = DecompressionMethods.GZip) Console.WriteLine(await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync()); } } } }
温馨提示: 本文由Jm博客推荐,转载请保留链接: https://www.jmwww.net/file/65418.html

