浅析C#中的“==”和Equals
标签:
1.“==”和Equals两个真的有关联吗?对于“==”和Equals大多数网友都是这样总结的:
“==” 是比较两个变量的值相等。
Equals是比较两个变量是否指向同一个对象。
如:这篇文章,并以这篇文章中的例子为例。
public class Person { public Person(string name) { this.Name = name; } public string Name { get; set; } } static void Main(string[] args) { string a = new string(new char[] { ‘h‘, ‘e‘, ‘l‘, ‘l‘, ‘o‘ }); string b = new string(new char[] { ‘h‘, ‘e‘, ‘l‘, ‘l‘, ‘o‘ }); Console.WriteLine(a == b); //true Console.WriteLine(a.Equals(b)); //true object g = a; object h = b; Console.WriteLine(g == h); //false Console.WriteLine(g.Equals(h)); //true Person p1 = new Person("jia"); Person p2 = new Person("jia"); Console.WriteLine(p1 == p2); //false Console.WriteLine(p1.Equals(p2)); //false Person p3 = new Person("jia"); Person p4 = p3; Console.WriteLine(p3 == p4); //true Console.WriteLine(p3.Equals(p4)); //true Console.ReadKey(); }
假如上述结论正确,“==” 是比较两个变量值相等,那么下面这句代码就不应该为True.
Console.WriteLine(a == b); //true
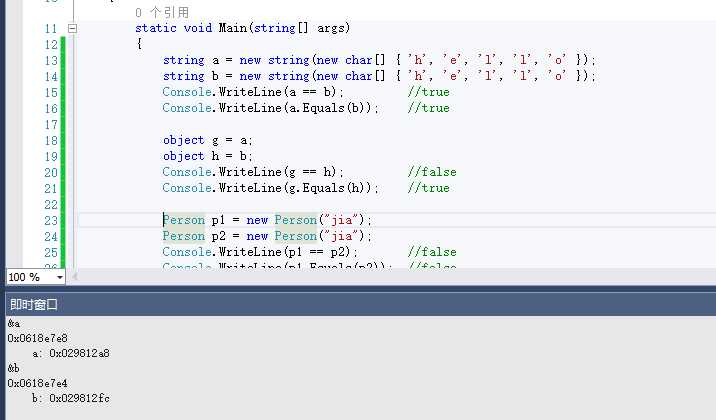
很明显,上面的两个字符串变量:a,b 是指向两个不同的对象,即它们在栈空间存储的内存地址也是不同的。但为毛它们就相等了呢?
2.什么是运算符重载?运算符重载,就是对已有的运算符重新进行定义,赋予其另一种功能,以适应不同的数据类型。打个简单的比方:“+” 运算符,在“+” 两
边全为数值类型的变量时,“+” 运算符表示数学上的“+” 意义。若“+” 运算符两边只要有一个为字符串类型,那么“+” 运算符就表示连接
字符串的意义。这样的运算符重载实例有很多,那么这跟本文主题有毛关系?我想说的是,上面字符串变量:a , b 就是因为String类
重载了运算符 “==”,看下列源代码:
public static bool operator == (String a, String b) { return String.Equals(a, b); } public static bool operator != (String a, String b) { return !String.Equals(a, b); }
很明显String类中真的重载了“==”运算符,并且不止 “==” 还有 “!=” 哦。并且在重载运算符方法内部直接调用String类中的Equals方法,
源代码如下:
public static bool Equals(String a, String b) { if ((Object)a==(Object)b) { return true; } if ((Object)a==null || (Object)b==null) { return false; } if (a.Length != b.Length) return false; return EqualsHelper(a, b); }
由上可得:“==” 运算符并不一定是比较两个变量中存储的值是否相等,这要看当前运算符在当前这个类型中是否写有重载。
3.Equals的重写还是上面例子:
string a = new string(new char[] { ‘h‘, ‘e‘, ‘l‘, ‘l‘, ‘o‘ }); string b = new string(new char[] { ‘h‘, ‘e‘, ‘l‘, ‘l‘, ‘o‘ }); Console.WriteLine(a == b); //true Console.WriteLine(a.Equals(b)); //true
由上可知:a ,b 为两个不同的对象。但Equals为True,则上述:“Equals是比较两个变量是否指向同一个对象“这一结论不成立。原因
看String类中的Equals方法:
public override bool Equals(Object obj)
{
if (this == null)
//this is necessary to guard against reverse-pinvokes and
throw new NullReferenceException(); //other callers who do not use the callvirt instruction
String str = obj as String;
if (str == null)
return false;
if (Object.ReferenceEquals(this, obj))
return true;
if (this.Length != str.Length)
return false;
return EqualsHelper(this, str);
}
public bool Equals(String value)
{
if (this == null)
//this is necessary to guard against reverse-pinvokes and
throw new NullReferenceException(); //other callers who do not use the callvirt instruction
if (value == null)
return false;
if (Object.ReferenceEquals(this, value))
return true;
if (this.Length != value.Length)
return false;
return EqualsHelper(this, value);
}
由上面可知String类中不仅重写了Object中的Equals还有自己的Equals方法,但是实现代码几乎是一样的。比较类型,内存地址,
实际值,从而获得最终的结果。所以Equals不一定就是单一的比较引用地址是否相同,更何况我们还可以重写和自定义。但是重写
Equals也有需要注意的地方,就是如果你需要用到HashMap,HashSet,Hashtable那么你也需要重写GetHashCode()。
4.为什么有了“==”还要有Equals?温馨提示: 本文由Jm博客推荐,转载请保留链接: https://www.jmwww.net/file/70322.html


